Compare E4CV 4-circle orientation with SPEC fourc#
Following the E4CV example (consult the example for geometry details), compare the orientation matix and positioning operations with hklpy (and libhkl) and SPEC.
Information from a SPEC data file will be used for the comparison.
Note: This example is available as a Jupyter notebook from the hklpy source code website: bluesky/hklpy
In SPEC fourc geometry (https://certif.com/spec_help/fourc.html):
name |
mnemonic |
description |
|---|---|---|
2theta |
tth |
Detector arm rotation |
Omega |
om |
Rotates sample circles |
Chi |
chi |
Sample tilt |
Phi |
phi |
Sample rotation |
The provided SPEC data file names these motors: tth, th, chi, phi so this example will use the same names to help the comparison.
[1]:
# mapping of axis names between hklpy and SPEC
AXIS_NAME_MAP = dict(
# E4CV fourc
tth='tth', # Detector arm rotation
omega='th', # Rotates chi around horizontal axis
chi='chi', # TODO: Rotates phi around beam axis # TODO: is this correct?
phi='phi', # Sample rotation around horizontal axis (when phi is co-linear with omega)
)
Read the SPEC scan from the data file#
The SPEC file provides all the information needed here. The spec2nexus (python) package can read the file and parse the content into useful structures, including deducing the diffractometer geometry in many cases.
[2]:
import pyRestTable
from spec2nexus.spec import SpecDataFile
specfile = SpecDataFile("resources/LNO_LAO_s14.dat")
specscan = specfile.getScan(14)
spec_d = specscan.diffractometer
spec_d.UB = spec_d.geometry_parameters["ub_matrix"][2]
terms = {
"SPEC file": specfile.specFile,
"scan #": specscan.scanNum,
"SPEC scanCmd": specscan.scanCmd,
"geometry": spec_d.geometry_name,
"mode": spec_d.mode,
"lattice": spec_d.lattice,
"wavelength": spec_d.wavelength,
"reflection 1": spec_d.reflections[0],
"reflection 2": spec_d.reflections[1],
"[UB]": spec_d.UB,
}
tbl = pyRestTable.Table()
tbl.labels = "term value".split()
for k, v in terms.items():
tbl.addRow((k, v))
print(tbl)
============ =========================================================================================================================================================
term value
============ =========================================================================================================================================================
SPEC file LNO_LAO
scan # 14
SPEC scanCmd hklscan 1.00133 1.00133 1.00133 1.00133 2.85 3.05 200 -400000
geometry fourc
mode Omega equals zero
lattice LatticeParameters3D(a=3.781726143, b=3.791444574, c=3.79890313, alpha=90.2546203, beta=90.01815424, gamma=89.89967858)
wavelength 1.239424258
reflection 1 Reflections3D(h=0.0, k=0.0, l=2.0, wavelength=1.239424258, angles=OrderedDict([('tth', 38.09875), ('th', 19.1335), ('chi', 90.0135), ('phi', 0.0)]))
reflection 2 Reflections3D(h=1.0, k=1.0, l=3.0, wavelength=1.239424258, angles=OrderedDict([('tth', 65.644), ('th', 32.82125), ('chi', 115.23625), ('phi', 48.1315)]))
[UB] [[-1.65871244e+00 9.82002413e-02 -3.89705578e-04]
[-9.55499031e-02 -1.65427863e+00 2.42844486e-03]
[ 2.62981891e-04 9.81574682e-03 1.65396181e+00]]
============ =========================================================================================================================================================
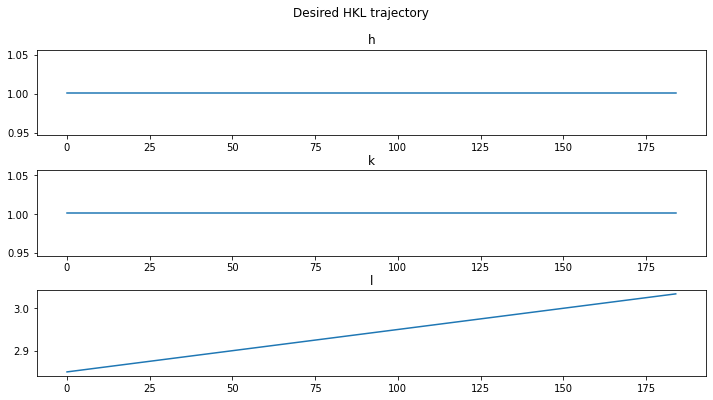
Plot the (hkl) trajectories in the scan#
[3]:
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# plot the h, k, & l vs. point number
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(12, 6))
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.4, wspace=0.2)
plt.suptitle('Desired HKL trajectory')
axes[0].plot(specscan.data["H"])
axes[0].set_title("h")
axes[1].plot(specscan.data["K"])
axes[1].set_title("k")
axes[2].plot(specscan.data["L"])
axes[2].set_title("l")
plt.show()
Setup the E4CV diffractometer in hklpy#
[4]:
from hkl import SimulatedE4CV
from hkl import Lattice
Use the hkl.geometries.SimulatedE4CV() class. All is prebuilt.
[5]:
class Diffractometer(SimulatedE4CV):
pass
[6]:
fourc = Diffractometer("", name="fourc")
fourc.calc.physical_axis_names = {
# E4CV: local
'omega': 'th',
'chi': 'chi',
'phi': 'phi',
'tth': 'tth',
}
[7]:
# add the sample to the calculation engine
fourc.calc.new_sample(
specfile.specFile,
lattice=Lattice(
a=spec_d.lattice.a,
b=spec_d.lattice.b,
c=spec_d.lattice.c,
alpha=spec_d.lattice.alpha,
beta=spec_d.lattice.beta,
gamma=spec_d.lattice.gamma)
)
[7]:
HklSample(name='LNO_LAO', lattice=LatticeTuple(a=3.781726143, b=3.791444574, c=3.79890313, alpha=90.2546203, beta=90.01815424, gamma=89.89967858), ux=Parameter(name='None (internally: ux)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.0, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), uy=Parameter(name='None (internally: uy)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.0, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), uz=Parameter(name='None (internally: uz)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.0, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), U=array([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]]), UB=array([[ 1.66146225e+00, -2.89938471e-03, 5.11196668e-04],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 1.65721725e+00, 7.34922202e-03],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.65394723e+00]]), reflections=[])
Test hklpy with the UB orientation matrix from SPEC#
Using the UB matrix as provided in the SPEC data file, compute the forward reflection positions and compare with those calculated by libhkl.
[8]:
# get the UB matrix from the SPEC data
# SPEC's UB first row moved (via numpy slicing) to last row for hklpy
fourc.UB.put(spec_d.UB[[1,2,0], :])
print(spec_d.UB)
print(fourc.UB.get())
# calculate angles with hklpy using the SPEC UB matrix
fourc.engine.mode = "bissector"
fourc.calc["phi"].limits = (-50, 100)
fourc.calc["tth"].limits = (-2, 180)
print("(002) :", fourc.forward((0, 0, 2)))
print("(113) :", fourc.forward((1, 1, 3)))
[[-1.65871244e+00 9.82002413e-02 -3.89705578e-04]
[-9.55499031e-02 -1.65427863e+00 2.42844486e-03]
[ 2.62981891e-04 9.81574682e-03 1.65396181e+00]]
[[-9.55499053e-02 -1.65427875e+00 2.42825603e-03]
[ 2.63161907e-04 9.81566638e-03 1.65396189e+00]
[-1.65871254e+00 9.82003048e-02 -3.89644168e-04]]
(002) : PosCalcE4CV(th=23.915206114843656, chi=89.91480547663566, phi=99.11611601203889, tth=47.83041222968731)
(113) : PosCalcE4CV(th=42.331294286006255, chi=115.20291094237977, phi=48.13306144010148, tth=84.66258857201251)
Define a custom reporting function to format the output table.
[9]:
def add_ref_to_table(tbl, r):
sol = fourc.forward((r.h, r.k, r.l))
nm = f"{r.h:.0f} {r.k:.0f} {r.l:.0f}"
# print(nm, sol)
for sm in AXIS_NAME_MAP.values():
row = [f"({nm})", sm]
v_hklpy = getattr(sol, sm)
v_spec = r.angles[sm]
row.append(f"{v_hklpy:.5f}")
row.append(f"{v_spec:.5f}")
row.append(f"{v_hklpy-v_spec:.5f}")
tbl.addRow(row)
For each of the orientation reflections used in the SPEC file, report the computed motor positions for each reflection for E4CV and SPEC. We’ll only pick positions where \(2\theta\ge 0\).
[10]:
# Compare these angles with those from SPEC
tbl = pyRestTable.Table()
tbl.labels = "(hkl) motor E4CV SPEC difference".split()
r1, r2 = spec_d.reflections
fourc.engine.mode = "bissector"
fourc.calc["tth"].limits = (-2, 180)
add_ref_to_table(tbl, r1)
# print(r2)
add_ref_to_table(tbl, r2)
print(tbl)
======= ===== ========= ========= ==========
(hkl) motor E4CV SPEC difference
======= ===== ========= ========= ==========
(0 0 2) tth 47.83041 38.09875 9.73166
(0 0 2) th 23.91521 19.13350 4.78171
(0 0 2) chi 89.91481 90.01350 -0.09869
(0 0 2) phi 99.11612 0.00000 99.11612
(1 1 3) tth 84.66259 65.64400 19.01859
(1 1 3) th 42.33129 32.82125 9.51004
(1 1 3) chi 115.20291 115.23625 -0.03334
(1 1 3) phi 48.13306 48.13150 0.00156
======= ===== ========= ========= ==========
Note that the angles do not match between E4CV and SPEC, even if we re-arrange the rows as we did above. Can’t just use the UB matrix from the one program in the other software.
Need to add the orientation reflections (with wavelength), then compute the UB matrix. Follow in the section below.
Setup the UB orientation matrix using hklpy#
Compute the UB matrix using hklpy (& libhkl).
[11]:
fourc.calc.wavelength = 1.239424258 # Angstrom
refs = [
fourc.calc.sample.add_reflection(
r.h, r.k, r.l,
position=fourc.calc.Position(
tth=r.angles["tth"],
th=r.angles["th"],
chi=r.angles["chi"],
phi=r.angles["phi"],
)
)
for r in spec_d.reflections
]
fourc.calc.sample.compute_UB(*refs)
tbl = pyRestTable.Table()
tbl.labels = "term value".split()
tbl.addRow(("SPEC [UB]", spec_d.UB))
tbl.addRow(("E4CV [UB]", fourc.UB.get()))
print(tbl)
========= ===================================================
term value
========= ===================================================
SPEC [UB] [[-1.65871244e+00 9.82002413e-02 -3.89705578e-04]
[-9.55499031e-02 -1.65427863e+00 2.42844486e-03]
[ 2.62981891e-04 9.81574682e-03 1.65396181e+00]]
E4CV [UB] [[-9.55498634e-02 -1.65427875e+00 2.42844498e-03]
[ 2.63111155e-04 9.81585901e-03 1.65396189e+00]
[-1.65871254e+00 9.82002627e-02 -3.89705597e-04]]
========= ===================================================
Report the results, as before, and compare with table above.
[12]:
tbl = pyRestTable.Table()
tbl.labels = "term value".split()
tbl.addRow(("energy, keV", fourc.calc.energy))
tbl.addRow(("wavelength, angstrom", fourc.calc.wavelength))
tbl.addRow(("position", fourc.position))
tbl.addRow(("sample name", fourc.sample_name.get()))
tbl.addRow(("[U]", fourc.U.get()))
tbl.addRow(("[UB]", fourc.UB.get()))
tbl.addRow(("lattice", fourc.lattice.get()))
print(tbl)
print(f"sample\t{fourc.calc.sample}")
==================== =========================================================================
term value
==================== =========================================================================
energy, keV 10.003370322932636
wavelength, angstrom 1.239424258
position DiffractometerPseudoPos(h=-0.0, k=0.0, l=0.0)
sample name LNO_LAO
[U] [[-5.75094968e-02 -9.98327391e-01 5.92267768e-03]
[ 1.58361191e-04 5.92337392e-03 9.99982444e-01]
[-9.98344947e-01 5.75094251e-02 -1.82553939e-04]]
[UB] [[-9.55498634e-02 -1.65427875e+00 2.42844498e-03]
[ 2.63111155e-04 9.81585901e-03 1.65396189e+00]
[-1.65871254e+00 9.82002627e-02 -3.89705597e-04]]
lattice [ 3.78172593 3.7914443 3.79890295 90.25465556 90.01815877 89.89967654]
==================== =========================================================================
sample HklSample(name='LNO_LAO', lattice=LatticeTuple(a=3.781725931569308, b=3.79144430103082, c=3.798902949497184, alpha=90.25465555509926, beta=90.01815876717824, gamma=89.89967653973522), ux=Parameter(name='None (internally: ux)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=-90.01045975373877, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), uy=Parameter(name='None (internally: uy)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.3393464183946019, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), uz=Parameter(name='None (internally: uz)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=93.2969283549115, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), U=array([[-5.75094968e-02, -9.98327391e-01, 5.92267768e-03],
[ 1.58361191e-04, 5.92337392e-03, 9.99982444e-01],
[-9.98344947e-01, 5.75094251e-02, -1.82553939e-04]]), UB=array([[-9.55498634e-02, -1.65427875e+00, 2.42844498e-03],
[ 2.63111155e-04, 9.81585901e-03, 1.65396189e+00],
[-1.65871254e+00, 9.82002627e-02, -3.89705597e-04]]), reflections=[(h=0.0, k=0.0, l=2.0), (h=1.0, k=1.0, l=3.0)], reflection_measured_angles=array([[0. , 0.44139322],
[0.44139322, 0. ]]), reflection_theoretical_angles=array([[0. , 0.44081129],
[0.44081129, 0. ]])))
[13]:
# Compare these angles with those from SPEC
# fourc.calc["phi"].limits = (-1, 100)
tbl = pyRestTable.Table()
tbl.labels = "(hkl) motor E4CV SPEC difference".split()
r1, r2 = spec_d.reflections
fourc.calc["tth"].limits = (-2, 180)
fourc.engine.mode = "constant_phi"
fourc.phi.move(0)
add_ref_to_table(tbl, r1)
fourc.engine.mode = "bissector"
add_ref_to_table(tbl, r2)
print(tbl)
======= ===== ========= ========= ==========
(hkl) motor E4CV SPEC difference
======= ===== ========= ========= ==========
(0 0 2) tth 38.08407 38.09875 -0.01468
(0 0 2) th 19.12616 19.13350 -0.00734
(0 0 2) chi 90.01350 90.01350 0.00000
(0 0 2) phi 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000
(1 1 3) tth 65.63700 65.64400 -0.00700
(1 1 3) th 32.81850 32.82125 -0.00275
(1 1 3) chi 115.20291 115.23625 -0.03334
(1 1 3) phi 48.13305 48.13150 0.00155
======= ===== ========= ========= ==========