NSLS-II TARDIS Configuration#
This notebook documents some calculations using a simulation of the Tardis diffractometer (an E6C variation) at NSLS-II. The connections with the EPICS motors have been replaced with simulated motors for this example.
Using the E6C geometry from libhkl, @cmazzoli found that, in this geometry, with the “lifting_detector_mu” mode, the following mapping applies:
libhkl |
TARDIS |
|---|---|
mu |
theta |
gamma |
delta |
delta |
gamma |
phi |
None |
chi |
None |
omega |
None |
The diffractometer geometry with angle and axis definitions are depicted below
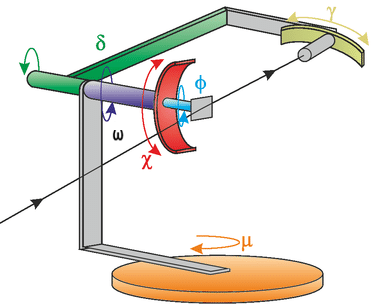
libhkl documentation of the E6C (Eulerian 6-circle) geometry
Begin by instantiating a calculation engine of the appropriate geometry, and configuring its mode as lifting_detector_mu . We must reach into the hkl.calc module to import CalcE6C.
[1]:
from hkl.calc import CalcE6C
tardis_calc = CalcE6C()
# what modes are available?
print(f"Available modes: {tardis_calc.engine.modes = }")
print(f"{tardis_calc.physical_axes = }")
print(f"{tardis_calc.pseudo_axes = }")
Available modes: tardis_calc.engine.modes = ['bissector_vertical', 'constant_omega_vertical', 'constant_chi_vertical', 'constant_phi_vertical', 'lifting_detector_phi', 'lifting_detector_omega', 'lifting_detector_mu', 'double_diffraction_vertical', 'bissector_horizontal', 'double_diffraction_horizontal', 'psi_constant_vertical', 'psi_constant_horizontal', 'constant_mu_horizontal']
tardis_calc.physical_axes = OrderedDict([('mu', 0.0), ('omega', 0.0), ('chi', 0.0), ('phi', 0.0), ('gamma', 0.0), ('delta', 0.0)])
tardis_calc.pseudo_axes = OrderedDict([('h', 0.0), ('k', 0.0), ('l', 0.0)])
[2]:
tardis_calc.engine.mode = 'lifting_detector_mu'
Next, seed the calculation engine with a parameterized sample and wavelength (or energy).
NOTE: length units are in Angstrom, angles are in degrees, and energy is in keV.
[3]:
from hkl import Lattice
# lattice cell lengths are in Angstrom, angles are in degrees
lattice = Lattice(a=9.069, b=9.069, c=10.390, alpha=90.0, beta=90.0, gamma=120.0)
sample = tardis_calc.new_sample('sample1', lattice=lattice)
print(f"{sample = }")
sample = HklSample(name='sample1', lattice=LatticeTuple(a=9.069, b=9.069, c=10.39, alpha=90.0, beta=90.0, gamma=119.99999999999999), ux=Parameter(name='None (internally: ux)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.0, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), uy=Parameter(name='None (internally: uy)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.0, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), uz=Parameter(name='None (internally: uz)', limits=(min=-180.0, max=180.0), value=0.0, fit=True, inverted=False, units='Degree'), U=array([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]]), UB=array([[ 7.99999720e-01, 3.99999860e-01, -6.41365809e-17],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 6.92820080e-01, -6.41365809e-17],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 6.04733908e-01]]), reflections=[])
[4]:
tardis_calc.wavelength = 1.61198 # in Angstrom
# just to check
print(f"Energy: {tardis_calc.energy = } keV")
Energy: tardis_calc.energy = 7.691422871251505 keV
Now, apply constraints appropriate for TARDIS’ geometry. This includes setting limits on the acceptable ranges of motion, initial (and constant!) values, and whether or not a particular axis should be factored into the fitting function that produces the forward and inverse solutions.
Since we are working with a hkl.calc.CalcRecip object, we do not have access to the convenience of the apply_constraints() method provided by the hkl.diffract.Diffractometer class. We have to set the constraints the hard way. These are the same steps implemented within apply_constraints().
NOTE: physical motors should be checked that limits are in place prior to initiating any motion. Note also that none of the calculations below are associated with any physical motors, and that there is no connection between “limit” values used in the calculation, and soft-limit values that may be present in a control system for physical motors.
[5]:
# Theta
mu = tardis_calc['mu']
mu.limits = (-181, 181)
mu.value = 0
# we don't have it. Fix to 0
phi = tardis_calc['phi']
phi.limits = (0, 0)
phi.value = 0
# we don't have it. Fix to 0
chi = tardis_calc['chi']
chi.limits = (0, 0)
chi.value = 0
# we don't have it!! Fix to 0
omega = tardis_calc['omega']
omega.limits = (0, 0)
omega.value = 0
# NOTE: Tardis detector stage names are swapped from canonical names!
# delta
gamma = tardis_calc['gamma']
gamma.limits = (-5, 180)
gamma.value = 0
# gamma
delta = tardis_calc['delta']
delta.limits = (-5, 180)
delta.value = 0
We can take a look at the UB matrix, but thus far, it won’t be very interesting
[6]:
print(f"{tardis_calc.sample.UB = }")
tardis_calc.sample.UB = array([[ 7.99999720e-01, 3.99999860e-01, -6.41365809e-17],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 6.92820080e-01, -6.41365809e-17],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 6.04733908e-01]])
Add two, known reflections and the motor positions associated with those hkl values. Here, we are using values from @cmazolli’s ESRF notes:
(3,3,0): del = 64.449, gam = -0.871, th = 25.285
(5,2,0): del = 79.712, gam = -1.374, th = 46.816
NOTE: the translation of gamma==delta, delta==gamma, and mu==theta is being used
[7]:
r1 = tardis_calc.sample.add_reflection(3, 3, 0,
position=tardis_calc.Position(gamma=64.449, mu=25.285, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, omega=0.0, delta=-0.871))
r2 = tardis_calc.sample.add_reflection(5, 2, 0,
position=tardis_calc.Position(gamma=79.712, mu=46.816, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, omega=0.0, delta=-1.374))
[8]:
print(f"{tardis_calc.sample.reflections = }")
tardis_calc.sample.reflections = [(h=3.0, k=3.0, l=0.0), (h=5.0, k=2.0, l=0.0)]
Now a UB matrix can be computed.
[9]:
tardis_calc.sample.compute_UB(r1, r2)
[9]:
array([[ 0.31323551, -0.4807593 , 0.01113654],
[ 0.73590724, 0.63942704, 0.01003773],
[-0.01798898, -0.00176066, 0.60454803]])
Compare some libhkl-generated results with those from @cmazolli’s notes:
# Experimentally found reflections @ Lambda = 1.61198 A
# (4, 4, 0) = [90.628, 38.373, 0, 0, 0, -1.156]
# (4, 1, 0) = [56.100, 40.220, 0, 0, 0, -1.091]
# @ Lambda = 1.60911
# (6, 0, 0) = [75.900, 61.000, 0, 0, 0, -1.637]
# @ Lambda = 1.60954
# (3, 2, 0) = [53.090, 26.144, 0, 0, 0, -.933]
# (5, 4, 0) = [106.415, 49.900, 0, 0, 0, -1.535]
# (4, 5, 0) = [106.403, 42.586, 0, 0, 0, -1.183]
[10]:
print(f"{tardis_calc.forward((4,4,0)) = }")
tardis_calc.forward((4,4,0)) = (PosCalcE6C(mu=38.37622128052063, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=90.63030469353308, delta=-1.1613181970939916),)
[11]:
print(f"{tardis_calc.forward((4,1,0)) = }")
tardis_calc.forward((4,1,0)) = (PosCalcE6C(mu=40.219919777570965, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=56.09704093977083, delta=-1.0836608655032929),)
Change wavelength here to 1.60911 Angstrom. Note the difference below in delta (TARDIS’ gamma axis)
[12]:
# change wavelength (Angstrom)
tardis_calc.wavelength = 1.60911
print(f"{tardis_calc.forward((6,0,0)) = }")
tardis_calc.forward((6,0,0)) = (PosCalcE6C(mu=60.99346591074179, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=75.84521749189145, delta=-1.5839501607961701),)
[13]:
tardis_calc.wavelength = 1.60954
print(f"{tardis_calc.forward((3,2,0)) = }")
print(f"{tardis_calc.forward((5,4,0)) = }")
print(f"{tardis_calc.forward((4,5,0)) = }")
tardis_calc.forward((3,2,0)) = (PosCalcE6C(mu=26.173823521308144, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=53.05207622287554, delta=-0.8437995840438257),)
tardis_calc.forward((5,4,0)) = (PosCalcE6C(mu=49.892322604056034, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=106.32053081067252, delta=-1.423656049079967),)
tardis_calc.forward((4,5,0)) = (PosCalcE6C(mu=42.54926633295045, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=106.31894239326303, delta=-1.1854071532601609),)
HKL PseudoPositioner Use#
Let’s explore the idea of an hkl ‘motor’
[14]:
from ophyd import Component as Cpt
from ophyd import (PseudoSingle, EpicsMotor)
from hkl import SimulatedE6C
# FIXME: hack to get around what should have been done at init of tardis_calc instance
tardis_calc._lock_engine = True
class Tardis(SimulatedE6C): ...
# class Tardis(E6C):
# h = Cpt(PseudoSingle, '')
# k = Cpt(PseudoSingle, '')
# l = Cpt(PseudoSingle, '')
# theta = Cpt(EpicsMotor, 'XF:31IDA-OP{Tbl-Ax:X1}Mtr')
# omega = Cpt(EpicsMotor, 'XF:31IDA-OP{Tbl-Ax:X2}Mtr')
# chi = Cpt(EpicsMotor, 'XF:31IDA-OP{Tbl-Ax:X3}Mtr')
# phi = Cpt(EpicsMotor, 'XF:31IDA-OP{Tbl-Ax:X4}Mtr')
# delta = Cpt(EpicsMotor, 'XF:31IDA-OP{Tbl-Ax:X5}Mtr')
# gamma = Cpt(EpicsMotor, 'XF:31IDA-OP{Tbl-Ax:X6}Mtr')
# re-map Tardis' axis names onto what an E6C expects
name_map = {
# tardis: E6C
'mu': 'theta',
'omega': 'omega',
'chi': 'chi',
'phi': 'phi',
'gamma': 'delta',
'delta': 'gamma',
}
tardis = Tardis(
'', # no prefix
name='tardis', # local name
calc_inst=tardis_calc, # the calc engine setup above
# energy=tardis_calc.energy, # FIXME: unexpected keyword argument
)
tardis.calc.physical_axis_names = name_map
print(f"{tardis.calc.physical_axis_names = }")
tardis.calc.physical_axis_names = ['theta', 'omega', 'chi', 'phi', 'delta', 'gamma']
[15]:
print(f"{tardis.real_position = }")
tardis.real_position = TardisRealPos(mu=0, omega=0, chi=0, phi=0, gamma=0, delta=0)
[16]:
print(f"{tardis.connected = }")
tardis.connected = True
[17]:
print(f"Energy: {tardis.energy.get() = } keV")
Energy: tardis.energy.get() = 8.0 keV
Move to (101) reflection#
[18]:
tardis.move((1,0,1), wait=False)
[18]:
MoveStatus(done=False, pos=tardis, elapsed=0.0, success=False, settle_time=0.0)
[19]:
status = _
[20]:
print(f"{status.done = }")
status.done = True
[21]:
print(f"{tardis.real_position = }")
tardis.real_position = TardisRealPos(mu=32.61342481972243, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=12.011255441335317, delta=8.64179902840924)
[22]:
print(f"{tardis.position = }")
tardis.position = TardisPseudoPos(h=1.0000000000000002, k=-5.667215834780817e-16, l=1.0)
Move to (102) reflection#
[23]:
tardis.move((1,0,2))
[23]:
MoveStatus(done=True, pos=tardis, elapsed=0.0, success=True, settle_time=0.0)
[24]:
tardis.h.describe()
[24]:
OrderedDict([('tardis_h',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_h.position',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_h_setpoint',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_h.target',
'dtype': 'integer',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''})])
[25]:
tardis.h.read()
[25]:
OrderedDict([('tardis_h', {'value': 1.0, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9169118}),
('tardis_h_setpoint',
{'value': 1, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9169252})])
[26]:
tardis.describe()
[26]:
OrderedDict([('tardis_h',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_h.position',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_h_setpoint',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_h.target',
'dtype': 'integer',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_k',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_k.position',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_k_setpoint',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_k.target',
'dtype': 'integer',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_l',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_l.position',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_l_setpoint',
{'source': 'PY:tardis_l.target',
'dtype': 'integer',
'shape': [],
'upper_ctrl_limit': 0,
'lower_ctrl_limit': 0,
'units': ''}),
('tardis_mu',
{'source': 'computed',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'units': '',
'lower_ctrl_limit': -180,
'upper_ctrl_limit': 180}),
('tardis_omega',
{'source': 'computed',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'units': '',
'lower_ctrl_limit': -180,
'upper_ctrl_limit': 180}),
('tardis_chi',
{'source': 'computed',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'units': '',
'lower_ctrl_limit': -180,
'upper_ctrl_limit': 180}),
('tardis_phi',
{'source': 'computed',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'units': '',
'lower_ctrl_limit': -180,
'upper_ctrl_limit': 180}),
('tardis_gamma',
{'source': 'computed',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'units': '',
'lower_ctrl_limit': -180,
'upper_ctrl_limit': 180}),
('tardis_delta',
{'source': 'computed',
'dtype': 'number',
'shape': [],
'units': '',
'lower_ctrl_limit': -180,
'upper_ctrl_limit': 180})])
[27]:
tardis.read()
[27]:
OrderedDict([('tardis_h', {'value': 1.0, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9169118}),
('tardis_h_setpoint',
{'value': 1, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9169252}),
('tardis_k',
{'value': -1.0351079150284598e-17,
'timestamp': 1700539353.9170356}),
('tardis_k_setpoint',
{'value': 0, 'timestamp': 1700539353.917049}),
('tardis_l',
{'value': 1.9999999999999998, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9170997}),
('tardis_l_setpoint',
{'value': 2, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9171119}),
('tardis_mu',
{'value': 42.936333275662705, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9886892}),
('tardis_omega', {'value': 0.0, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9886923}),
('tardis_chi', {'value': 0.0, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9886947}),
('tardis_phi', {'value': 0.0, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9886968}),
('tardis_gamma',
{'value': 12.143148125839154, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9886992}),
('tardis_delta',
{'value': 17.765469685728892, 'timestamp': 1700539353.9887023})])
[28]:
print(f"{tardis.position = }")
tardis.position = TardisPseudoPos(h=1.0, k=-1.0351079150284598e-17, l=1.9999999999999998)
[29]:
print(f"{tardis.real_position = }")
tardis.real_position = TardisRealPos(mu=42.936333275662705, omega=0.0, chi=0.0, phi=0.0, gamma=12.143148125839154, delta=17.765469685728892)